You plug devices into wall outlets every day, but AC adapters do the critical conversion work you never see. Your laptop, phone, and router all run on direct current, yet your walls deliver alternating current at dangerously high voltages.
AC adapters solve this mismatch through precise electromagnetic transformation and rectification circuits. Inside each adapter, transformers, diodes, and capacitors work together through multiple stages. This conversion process delivers the exact voltage and current type your device's internal circuits demand for safe operation.
At Pacoli Power, we design reliable, travel-friendly chargers and adapters that keep your devices powered wherever you go. Our adapters handle global voltage ranges and demanding conditions so you never worry about being disconnected.
What Is The AC Adapter?

An AC adapter converts alternating current (AC) from your wall outlet into direct current (DC) that powers your electronic devices. You plug it into a standard 120V or 240V AC outlet, and it steps down the voltage to match your device's requirements, typically 5V, 9V, 12V, or 19V DC.
The adapter contains a transformer that reduces voltage and a rectifier circuit that changes AC's oscillating flow into steady DC power. Your laptop, phone, and router all need this conversion because their internal circuits run exclusively on direct current.
Without this voltage transformation and current conversion, your devices would fail immediately or suffer permanent damage from incompatible power input.
How Do AC Adapters Work?

Every modern electronic device relies on direct current (DC), while household outlets provide alternating current (AC). The AC adapter bridges this electrical gap through a complex yet efficient conversion process. Here’s how it works inside:
1. Input & Safety Protection
AC power first enters through the input terminal, where a fuse and EMI line filter suppress electrical interference and protect internal circuits from overcurrent and voltage spikes.
2. AC Rectification
The current then flows through a diode bridge, performing full-wave rectification. This process converts both halves of the AC waveform into pulsating DC, aligning current flow in a single direction.
3. Voltage Smoothing
Electrolytic capacitors act as energy reservoirs, storing and releasing charge to eliminate voltage ripples and produce a stable, continuous DC signal for further regulation.
4. Switching & Voltage Regulation
A high-frequency transistor rapidly switches current through a transformer using pulse-width modulation (PWM). This allows precise voltage control, higher efficiency, and reduced size compared to traditional linear adapters.
5. Output Filtering & Feedback Control
Inductors and capacitors at the output stage remove residual electrical noise. A feedback control circuit continuously monitors output voltage and current, adjusting switching patterns and activating protection mechanisms during overload or short-circuit events.
In essence, an AC adapter functions as a miniature switch-mode power supply (SMPS), converting high-voltage AC into clean, regulated DC with precision, safety, and efficiency.
What are the Features of AC adapters?

Modern AC adapters pack sophisticated technology into compact designs. They deliver precise voltage regulation, built-in safety mechanisms, and energy-efficient operation that protects both your devices and electrical infrastructure.
1. AC → DC Conversion
Your adapter steps down high-voltage wall voltage through a transformer to lower levels. Then it uses diode rectifiers to flip AC's alternating waves into pulsating DC. Capacitors smooth these pulses by storing and releasing energy. It creates a steady DC voltage that your devices need.
2. Performance in High-Altitude Environments
AC adapters face two critical challenges above 2000 meters: reduced cooling efficiency and increased arcing risk. Reduced air density transfers heat inefficiently. It causes internal components to run hotter and requires power output derating.
Lower air pressure also weakens the air's ability to prevent electrical arcing between high-voltage conductors. Adapters designed for high-altitude use incorporate larger internal spacing and enhanced thermal management to maintain safe, reliable operation.
3. Reliability & Stability
Modern AC adapters combine precision engineering with intelligent protection. They feature efficient AC-to-DC conversion, thermal stability, and adaptive voltage control.
Built-in safeguards like overcurrent and surge protection ensure long lifespan, steady power delivery, and reliable operation even under high-altitude or demanding electrical conditions.
4. Variety in Design for Different Applications
Depending on your needs, you can choose from wall-mount models for travel convenience, desktop adapters for high-power setups, or industrial units with waterproofing and insulation for harsh environments.
Need flexibility on the go? Look for interchangeable-plug adapters that handle multiple socket types. Prefer something ultra-compact? GaN-based designs deliver the same output with half the size and heat. Whatever the setup, there’s an adapter engineered precisely for your device and lifestyle.
What is the Difference Between AC and DC Adapters?
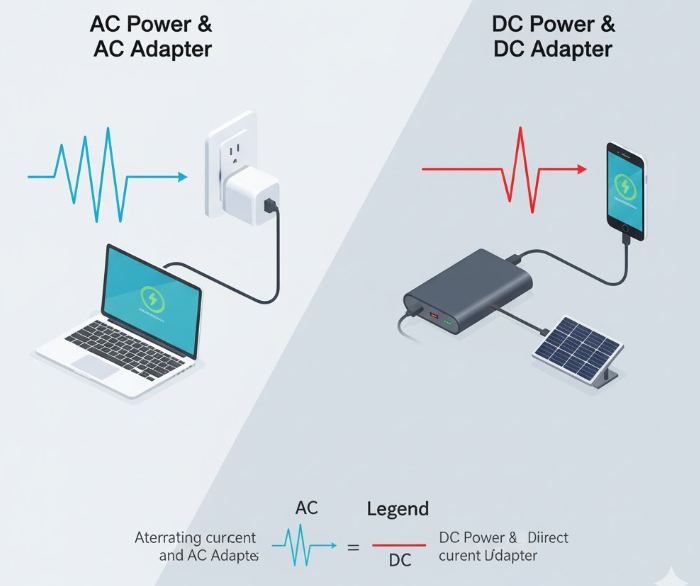
AC adapters convert alternating current (AC) from outlets into direct current (DC) for devices. On the contrary, DC adapters manage or convert existing DC voltage levels from one value to another. Both supply power, but their input, circuitry, and use cases differ.
In simple terms, AC power alternates direction, ideal for transmission over long distances. Whereas DC power flows steadily in one direction, ideal for sensitive electronics. Understanding this distinction ensures you select the correct adapter for your device’s electrical design.
| Feature | AC Adapter | DC Adapter |
| Input Source | Alternating Current (from wall outlets – 110V/220V AC) | Direct Current (from batteries, solar panels, or other DC sources) |
| Output Type | Converts AC to DC (AC → DC) | Regulates or converts one DC voltage to another (DC → DC) |
| Internal Components | Transformer, rectifier, filter, voltage regulator | Inverter, transformer, rectifier, regulator |
| Waveform | Alternating sinusoidal waveform | Constant, unidirectional linear flow |
| Usage | Common for laptops, routers, and consumer electronics | Used in automotive systems, solar setups, and battery-powered equipment |
| Efficiency & Size | Compact and efficient due to switching technology | Slightly less efficient when boosting voltage; often specialized |
| Example Device | Laptop charger (AC to DC) | Car USB adapter or DC-DC step-down converter |
Different Types of AC adapter

AC adapters come in multiple designs and configurations to suit diverse devices and environments. From wall-mount and desktop models to universal and industrial-grade units, each type offers unique power capacity, efficiency, and portability advantages.
| Type | Description | Typical Use |
| Desktop Adapter | Larger “brick-style” unit placed on the floor or desk | Desktop computers, printers |
| Wall Adapter | Compact unit plugs directly into wall | Laptops, tablets |
| Travel Adapter | Adapts plug shape between regions | International travel |
| Type C (European) | Universal European outlet compatibility | Continental Europe |
| Surge-Protected / Short-Circuit-Protected Adapters | Include safety circuits to prevent electrical damage | High-value electronics |
What Are The Different Types Of AC/DC Adapter Plug
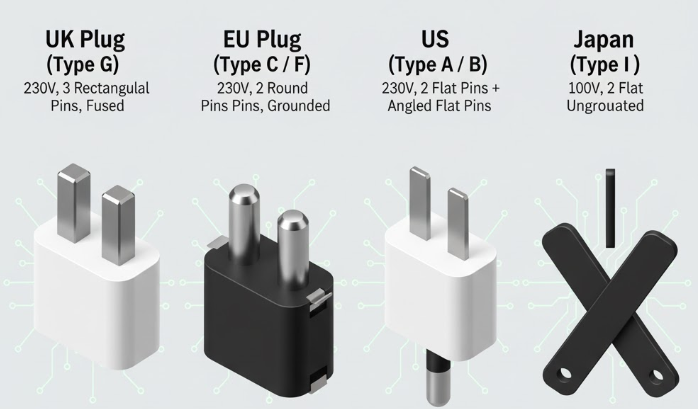
AC/DC adapter plugs are engineered to meet regional electrical standards, balancing safety, grounding, and voltage compatibility. Each plug type is optimized for its local power grid’s voltage, frequency, and insulation requirements to ensure safe, efficient power delivery.
UK Plug (Type G)
The UK plug features three rectangular pins arranged in a triangular formation. It operates on 230V at 50Hz and incorporates an internal fuse (usually 3A or 13A) for overcurrent protection.
Its grounded configuration ensures exceptional electrical safety and stability, making it ideal for heavy-duty electronics such as laptops, desktops, and industrial instruments.
EU Plug (Type C / Type F)
European plugs employ two round pins, supporting 230V at 50Hz power systems. Type C plugs are ungrounded and used for low-power devices, while Type F (Schuko) includes grounding clips for higher-load equipment.
Their slim, reversible design allows easy use across much of Europe, Asia, and parts of Africa, ensuring compatibility in multi-region travel adapters.
US Plug (Type A / Type B)
Standard in North America, this plug uses two flat parallel blades, with Type B adding a grounding pin for added protection. It runs on 120V at 60Hz, designed for lightweight consumer electronics.
Its polarized blade structure ensures correct orientation, minimizing electrical noise and enhancing safety in sensitive electronic circuits.
Australia Plug (Type I)
The Australian plug consists of three flat, angled blades and two active pins forming an inverted “V” and one vertical grounding pin. Operating on 230V at 50Hz, it’s widely used across Australia, New Zealand, and nearby regions. This configuration provides secure mechanical retention and strong contact reliability, minimizing arcing in high-load devices.
Japan Plug (Type A)
Japan’s plug resembles the US Type A but is rated for 100V at 50/60Hz, reflecting the country’s dual-frequency grid system. Its two flat blades with circular indentations ensure firm contact while maintaining compactness.
Primarily ungrounded, it’s ideal for portable electronics and precision devices that require stable, low-voltage DC conversion.
Electronic Devices That Use AC Adapters

Nearly every electronic device you own relies on an AC adapter to convert wall power into usable DC voltage.
Portable Computing Devices
Your laptop, tablet, and Chromebook all use external AC adapters because internal batteries store only DC power. These adapters typically deliver 19V, 12V, or 20V at 2-6 amps, depending on screen size and processor power.
Gaming laptops demand higher wattage (120-240W) compared to ultrabooks (45-65W) due to dedicated graphics cards and faster processors.
Mobile and Personal Electronics
Smartphone, smartwatch, wireless earbuds, and e-reader charge through AC adapters delivering 5V to 12V via USB connections. Modern fast-charging adapters use Power Delivery or Quick Charge protocols, stepping up voltage dynamically to push 18W-100W safely.
Fitness trackers and Bluetooth speakers use lower-power adapters (5W-15W) because their batteries are significantly smaller than phone batteries.
Office and Peripheral Equipment
Your printer, scanner, external monitor, and router each need dedicated AC adapters matched to their power requirements. Monitors typically use 12V or 19V adapters at 3-5 amps.
Routers run continuously on low-power 12V adapters consuming just 10-18W. Printers demand higher current during printing cycles, using adapters rated 24V-32V at 1-2 amps for heating elements and motor operation.
Entertainment and Multimedia Devices
Gaming console controllers, portable speakers, digital cameras, and streaming devices all depend on AC adapters. Camera chargers deliver precise 8.4V for lithium-ion battery chemistry.
Portable Bluetooth speakers use 5V USB adapters at 1-2 amps. Streaming sticks like Roku or Fire TV draw minimal power (5V at 1A) and often plug directly into TV USB ports as alternative power sources.
How to Select an AC Power Adapter for a Longer Lifespan?
Choosing the right AC adapter directly impacts your device's safety and the adapter's longevity. Five critical factors determine whether your adapter will last years or fail prematurely.
Match Electrical Specs
Your adapter's voltage must match your device exactly, even 0.5V difference can cause malfunction or damage. Check the amperage rating; your adapter should meet or exceed your device's current draw. A 3A adapter works fine for a 2A device, but never use a 1A adapter for 2A needs.
Pick Quality Brands
Reputable manufacturers use superior components like high-temperature capacitors and robust transformers that withstand years of daily use. Generic adapters cut costs through inferior parts that fail quickly. Look for certifications like UL, CE, or FCC marks proving the adapter meets safety standards and underwent rigorous testing.
Prioritize Cooling Features
Adapters with ventilation slots, heat sinks, or perforated casings dissipate heat more effectively than solid plastic enclosures. Heat degrades internal components rapidly, shortening lifespan dramatically. Choose adapters rated for higher efficiency (80%+) because they generate less waste heat during operation.
Look for Built-In Protections
Your adapter needs over-voltage protection (OVP), over-current protection (OCP), and short-circuit protection (SCP) to shut down instantly during faults. These circuits prevent damage to both the adapter and your device.
Check Input & Environment Range
Verify your adapter handles your region's voltage (100-240V for universal compatibility). Check the operating temperature range, quality adapters function reliably from 0°C to 40°C.
If you're at high altitude (above 2000m), confirm the adapter is rated for reduced air pressure to prevent overheating and arcing between internal components.
In Closing
AC adapters transform dangerous wall voltage into safe, stable DC power through transformer reduction, diode rectification, and capacitor smoothing. Quality adapters deliver precise voltage regulation, built-in safety protections, and efficient thermal management that extends lifespan significantly.
Matching electrical specifications, choosing reputable brands, and verifying environmental ratings protect your devices from damage and premature failure.
Ready to power your devices reliably anywhere? Explore Pacoli Power's collection of travel-ready adapters designed for global compatibility and lasting performance. Shop now and stay connected wherever your journey takes you.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: Can I use any AC adapter with my device?
Answer: No. Always match the voltage (V) and polarity precisely, and ensure the current (A) rating equals or exceeds your device’s requirement. Using the wrong adapter can cause overheating or permanent damage.
Question: Why does my AC adapter get warm during use?
Answer: Some warmth is normal during operation. However, excessive heat may signal overloading, inadequate ventilation, or internal wear. Ensure the adapter’s wattage suits your device’s power needs and keep it well-ventilated.
Question: What is a universal power adapter?
Answer: A universal adapter supports 100–240V input and features interchangeable plugs for multiple regions. It’s ideal for frequent travelers needing a single adapter for global compatibility and varied socket types.
Question: How long do AC adapters typically last?
Answer: Quality adapters generally last 5–10 years, depending on use and environment. Longevity improves with efficient heat management, premium capacitors, and avoiding exposure to moisture, dust, or power surges.
Question: What happens if my adapter’s polarity is reversed?
Answer: Reversed polarity can instantly damage circuits or prevent startup. Always confirm the center-positive or center-negative symbol matches between the adapter and device before connecting power.




